Audio
Music Production Suite 3 combines iZotope’s most powerful music production tools with their most musical stereo reverbs R4 and NIMBUS, plus a full year of in-depth tutorials from Groove3 — Featuring Ozone 9 Advanced, the comprehensive mastering suite, Neutron 3 Advanced for clear, focused mixes, the essential audio repair and restoration tools of RX 7 Standard, complete vocal production. If you are looking to buy iZotope RX 7 Audio Editor Advanced v7.01 then you have come to the right place to save big on retail price. Simply add iZotope RX 7 Audio Editor Advanced v7.01 or any other software titles to the shopping cart for even more volume savings and checkout easily.
Note
- Some hardware devices monopolize the audio drivers when sending audio clips to RX via RX Connect. If you are not able to hear the audio sent to RX from your DAW with RX Connect, change the audio driver to RX Monitor in the Driver type menu.
- Driver Type: Allows you to select a sound card driver model to use for playback and recording.
- Input/Output Device: Choose the device/sound card you want RX to use for playback and recording.
- Buffer Size: The total playback buffer size. In general, lowering these buffer sizes will improve meter responsiveness and lower latency, but increase CPU needs. Raising buffer sizes will lower CPU cost but increase latency. It’s worth exploring these ranges to find values that work best on your system.
- Num Buffers: Number of playback sub-buffers. (Windows MME Only.)
- Composite View gain reduction: Nondestructively reduces the output gain of all clips included in the Composite View tab by the amount specified in the dropdown.
- Channel Routing: For ASIO and CoreAudio drivers, click this button to choose which input and output channels RX uses. Click the Channel Routing button to open the Channel Routing dialog box.
- Configure Driver: Launches the manufacturer’s driver configuration dialog.
- Release when not in use: Auto-closes the audio device when playback in RX stops, freeing it for use in other audio applications. Disable this if playback from RX isn’t responsive enough.
- Test Tone: The test tone generator is useful for testing your speakers, audio hardware and listening environment. Tones at set frequencies or at a custom frequency can be used as test tones, as can white or pink noise. In addition, a Channel Identification mode will identify left and right speakers.
- Enable: Starts playback of a test tone.
- Type: Sets the type of test tone to play.
- Volume: Sets the volume of the test tone.
- Frequency: Sets the frequency of the test tone.
- Enable: Starts playback of a test tone.
- Output Gain: Output gain allows you to nondestructively adjust the playback level of RX 6 Audio Editor.
- IZotope Production Bundle/ Worth it??? Hi All, IZotope is offering me the Izotope Production Bundle for $99. I already own Ozone 7 Advanced, so what I would be acquiring that I don't already have is: Nectar 2 Production Suite Alloy 2 Trash 2 Expanded Is this worh $99 for these three? Thanks in Advance.
- If you use iZotope RX 2 or RX 2 Advanced, this series is a must have. By really knowing all the features and functions, as well as seeing it used on actual audio, there's nothing you won't be able to repair, enhance or manipulate with this amazing software. Get 'iZotope RX 2 Explained' today.
- Enter Acon Digital Acoustica 7.2. Then again, software is an extremely competitive market, thus viable alternatives to iZotope’s RX have emerged. Among them is Acon Digital’s Acoustica audio editor. Version 7.2, its latest release, comes with a very interesting stem splitting functionality that’s also AI-driven. According to the developer.
Display
- Show tooltips: When enabled, hovering over an RX feature with the mouse cursor will show a short description of the feature.
Display cursor coordinates in status bar: When enabled, the time coordinate of the cursor is shown in the status bar at the bottom of the RX main window. The amplitude of the audio at the cursor position and the frequency at the cursor position is also shown.
Show analog waveform: When digital audio is played back, it is converted to analog. The peak values in the analog waveform can be larger than the peaks in the digital waveform, leading to clipping in the output of a digital-to-analog converter. When Show analog waveform is enabled, RX will compute an analog waveform in the background. Any peaks will be highlighted in red on top of the existing digital waveform.
Note
RX will automatically display an analog waveform when zooming in at extreme zoom levels.
Offload waveform calculations: When enabled, RX’s waveform display will be computed in the background. This allows very large files to be loaded very quickly, but it slows down RX’s waveform displays.
Waveform interpolation order: If you zoom into the waveform so that individual samples become visible, RX will display an upsampled analog waveform as well as the individual digital samples. The interpolation order controls the quality of upsampling. Higher values yield more accurate analog waveforms at the expense of CPU usage.
Brightness: Adjusts the general brightness of the RX interface, allowing you to make RX more readable on your specific display.
Floating window opacity: Changes the opacity for RX’s floating windows. This can be useful if you wish to leave floating windows on top of the spectrogram and waveform without completely obscuring the display.
Keyboard

Customizing Keyboard Shortcuts
While RX includes default keyboard shortcuts, you can also customize them to your liking.
Refer to the Keyboard Shortcut Guide to reference a list of default RX key commands and find the internal shortcut command names used by RX. Referring to the guide can help you quickly identify the name of the key commands you want to customize and search for them in the “Show commands containing” field (explained below.)
- Presets: Save groups of key assignments with this tool.
- Show commands containing: Lets you search by keyword for a command you want to assign to a keystroke.
- Shortcuts for selected command: Shows if there are any keystrokes assigned to the command selected in the above menu.
- Remove: Removes the currently assigned keystroke from a command.
- Press Shortcut Key: To assign a new keystroke to a command, select the command from the menu, then click in this field and press a key or combination of keys.
- Assign: Assigns the entered keystroke to the current command. The shortcut will only be assigned to the current command if you press this button.
- Shortcut key currently used by: Lists commands that the current keystroke is assigned to.
Using the Alt modifier on Windows
On Windows systems, by default, “Alt + a letter” will open the corresponding menu for your currently open application. Alt + V for example will open RX’s View menu drop down. By default, none of RX’s shortcuts should conflict with these keyboard shortcuts, however if you wish to assign Alt + V to another operation, it will take precedence over the View menu.
Misc
- Session data folder: Allows you to choose a different folder to save RX’s temporary session data. These files are created to allow actions to be undone and sessions to be recalled in RX. Because these can be very large, it is best to set this to the drive on your computer with the most free space.
- Time scale frame rate: This sets the frame rate used to draw the time scale when RX is set to display the time code (see View menu or right-click the time ruler to change this setting). Choose from a list of standard frame rates or click in the combo box to define a custom frame rate.
- Default full-bandwidth paste mode: This controls RX’s behavior when pasting a full-bandwidth audio selection. Insert will move aside existing audio, Replace will overwrite existing audio, and Mix will add to existing audio.
- Default limited-bandwidth paste mode: Similar to the full-bandwidth paste mode, this controls RX’s behavior when pasting a limited-bandwidth audio selected.
- Resume last editing session when app starts: When enabled, RX will open all of the files (including edits, processing and undo history events) that were present when RX was last closed. Disabling this option will open the RX Audio Editor in its default state (no files loaded.)
- Automatically open files ending with .L and .R as split stereo: Mono audio files with (.L and .R) as well as (.1 and .2) extensions will be opened as stereo files when this option is enabled.
- Recall selections during undo/redo: When this is enabled, RX will recall the selection used for an item in the undo history. When stepping through the undo history events, selections that were used for each event will be restored along with the audio.
Disabling the selection undo/redo option
- Sometimes it is useful to turn this off if you need to compare undo history items and not break your current selection (like a useful loop).
- Sometimes it is useful to turn this off if you need to compare undo history items and not break your current selection (like a useful loop).
- Play only selected channels: If only a single channel of audio is selected and this option is enabled, all other channels will be muted during playback.
- Calculate RMS using AES-17: Uses the AES-17 1998 standard for RMS calculations (0 dB is a full scale sine wave) in the level meter, Waveform Statistics and Leveler modules. The other option is when 0 dB is the RMS of a full-scale square wave. These options differ by 3 dB.
- Pre- and Post-Roll during preview (ms): When Previewing audio processing in any module, the specified time amount will be added to the beginning and end of the previewed selection in order to provide contrast between unprocessed and preview-processed audio.
- Selection Feathering (ms): Allows for crossfading of processed and unprocessed audio when processing. If you need to make more precise edits, set this to 0.
Auth & Updates
Provides options to authorize or de-authorize RX (explained in the Authorization chapter), launch the iZotope Updater and choose how often the Updater automatically checks for updates.
Plug-ins
RX 6 Audio Editor supports the use of the following plug-in formats in the “Plug-in” module:
- VST 2: Windows and Mac
- AU (AudioUnit): Mac Only
- DirectX: Windows only
- Plug-in Lists: Displays plug-ins that have been scanned for use in the “Plug-in” hosting module of the RX Editor.
- Enable: Enables that plug-in format for use in the RX Audio Editor. This will trigger plug-in scanning to begin in the background.
Disable: Disables the associated plug-in format. This will clear the scanned plug-in list for that format. Re-enabling that plug-in format will prompt RX to re-scan that plug-in format.
Note
- If a plug-in failed scanning for any reason, the plug-in’s name will be prefixed with an error tag (ex: [Crashed] or [Failed]) to help troubleshoot the failure
- If a plug-in failed scanning for any reason, the plug-in’s name will be prefixed with an error tag (ex: [Crashed] or [Failed]) to help troubleshoot the failure
VST plug-in folders: Allows you to add or remove custom VST2 plug-in folder paths. RX uses the system VST2 plug-in folder by default. If you are using a custom directory for VST2 plug-ins, use this option to ensure that those VST2 plug-ins will be scanned.
Note about sub-folders when scanning for plug-ins
- RX will scan the first level of sub-folders in the custom VST2 folder. If some of your plug-ins do not show up when you scan them, and you know they’re in a subfolder of your plug-in folder, try moving them up one directory level.
- RX will scan the first level of sub-folders in the custom VST2 folder. If some of your plug-ins do not show up when you scan them, and you know they’re in a subfolder of your plug-in folder, try moving them up one directory level.
Group plug-ins by name in plug-in menus: When enabled, the RX plug-in menu will group plug-ins by common first words, usually the manufacturer’s name. When disabled, the RX plug-in menu will appear as a single, alphabetically sorted list.
Rescan: If RX detects that a plug-in is unstable, it will blacklist it and prevent it from being opened. The rescan option allows you to clear the blacklist of unsupported plug-ins and rescan all installed plug-ins in case an RX update or an update from the plug-in manufacturer resolves the issue.
- Sound Quality
- Ease of use
- Features
- Bang for buck
- Overall:
- Software: RX 5 Advanced Audio Editor
- Developer: iZotope
- Formats: Standalone application, VST, AU and AAX plug-ins for Mac and Windows.
- Price: Standard Version $349 - Advanced Version $1199 (US Dollars - MSRP)
- Demo: Fully functional for 14 days
- DRM: iLok (USB dongle not required)
- Website: https://www.izotope.com/en/products/audio-repair/rx/
Preamble
Having a set of audio repair tools is definitely one very desirable in most studios and on some they are just mandatory - any serious post-production facilities and mixing or mastering studios are bound to deal with damaged audio at some point. With that in mind, the question is: which one to choose? Fortunately for us this segment shows a busy yet not crowded marketplace, with a handful of great sounding and very capable solutions competing for attention but far from the over-saturated equalizer and dynamics segments. Having said that, the fact that not many developers put their efforts on making audio repair tools can be attributed to some extent to iZotope RX’s existence. Released back in 2008, RX simply took over. With an effective and powerful set of tools of the highest quality and a straightforward editor, iZotope pretty much dominated the market and although there are still some good competition out there, it’s safe to say that RX became a reference. We’ll go through it’s fifth iteration to see how far it goes in 2015 and if it manages to keep its crown. I’ll try to break down the editor’s major features, then do a brief run on the modules to wrap it all up in the end with scores.
The RX Audio Editor
RX’s audio editor features a clean layout with a very nice waveform and spectrogram display that can be customized to blend both visualization modes, offering a great deal of information about the amplitude and frequency of the audio material in place. The editor also features a clip-gain line, which provides very easy gain adjustment of the audio before it hits the modules. Right-section of the interface houses the modules - which I’ll go through in a moment and visualization options for frequency and amplitude. Lower section provides scrolling, further visualization and zoom controls, and the tools you need to select amplitude, frequency or time of the material and also a instant-process button that applies de-click, attenuate, fade, gain or spectral repair (replace) based upon common-use presets. This greatly speeds up the workflow and helps a lot if you’re dealing with lengthy material that needs a ton of small adjustments. Used in conjunction with the lasso tool it greatly straights up the process, allowing for quick repairs on the highlighted frequency, amplitude and time regions. Selection a region and right-clicking on the selection also brings up useful operations such as capturing the required frequency and amplitude information to feed specific modules that are based on frequency/amplitude “learning” functions such as EQ and Ambience match and De-noise. RX can also do audio recording with monitoring, which is good when doing restoration and archiving work since you can capture the material and keep everything within RX right from the very beginning. RX also comes with WAV, AIFF, FLAC, OGG import/export codecs so all bases (minus Apple codecs) are pretty much covered.
The RX modules and the Module Chain
Before I go through each module, I’d light to highlight one of the coolest RX features, the Module Chain, which lets the use combine multiple RX modules, providing a quick way to process audio with module-combos that you already know will work. I should mention that that the De-clip, De-click, De-crackle, De-hum, De-noise, De-Reverb and Dialogue De-noise modules are also offered as standalone as standalone plugins for your DAW, albeit at the cost of considerable latency and CPU resources on most cases. Nevertheless, it’s a welcome alternative to using the editor when you really need to deal with something live and/or with varying settings.
- De-clip: RX’s tool to deal with distortion problems is absurdly good and does some miracles on even the hottest and most clipped recordings you can come across. The layout is very intuitive and hard to get wrong, with some visual aid on the material’s amplitude, so it’s just a matter of setting the clipping level you want to address with the threshold slider and be amazed by the results! De-clip also features an optional make-up gain control and a peak limiter to keep things safe. Arguably one of the useful tools in RX’s arsenal and one that will likely get a lot of use when your sources are less than ideal, De-clip is a life saver. I found that applying it multiple times instead of going for a huge hit leads to better results and I couldn’t believe most things I was doing! Please ponderate my excitement a little bit and keep things in context within reason - this module will not save badly clipped mixes on a mastering situation, although it can definitely make them a lot more bearable and workable.
- De-click: Another miracle-maker, the De-click module can do a hell lot more than just plain click-removal. Along with the De-plosive module this is one of the best tools to deal with problematic sounds from syllables with “Ps” and “Bs” - just set the click type to “thump” and make things right! When used for it's meant purposes, it is simply the best solution I’ve found to this day to deal with a lot of flexible options to deal with all sorts of clicks, crackles, thumps and all sorts of short-bursts of crappiness that might’ve plagued a recording. I got very effect results using the frequency skew to nudge it towards low or high frequency attenuations and with the click widening options, which set operating length in milliseconds for the processing. It’s so effect that it’s scary, and it manages to remove the undesired and only the undesired, leaving the rest of the content rather untouched. A real lifesaver that could very well be a plugin on its own without any fear of the competition.
- De-hum: A set of notch and high-pass filters for cutting out electrical noise. The notch filters can act as cut-only parametric bands and the high-pass filter also features a variable slope, so in that regard De-hum can serve as general purpose and simple to use equalizer with all the quality one expects from iZotope.
- De-noise/Dialog De-noise: Another one that could definitely be a plugin on its own and it would be a very competitive entry in the noise-reduction segment. Extremely effective and versatile, coming in two operating modes: a broadband mode with the entire frequency spectrum and dialog/speech mode that is optimized for the frequency range of a human voice - this last mode also reveals itself as an excellent tool for removing or attenuating hiss from any kind recording, not only dialog. In that regard, I’ve found myself using Dialog De-noise a whole lot more since most of my noise problems occurred in the top end and on few occasions I had to resort to the full-spectrum mode.
- De-plosive (advanced only): This is a tool catered to the removal of the sounds associated with the excessive air coming from the Ps, Bs, Ts, Ks of the human voice that hurts microphones so much, especially on close-proximity situations. Very effective when used in conjunction with the De-click, the De-plosive can do wonders for a vocal track, setting up the terrain for the mixing stage, and needless to say that it is also great for cleaning up speech when pristine edits are needed.
- Spectral Repair: One of the most advanced (if not the most) module on RX, this tool provides cutting-edge processes to remove unwanted elements of the material such as footsteps, old chairs squeaks, mouth-related artifacts, buzzing alarms in the background and other noises and interferences that are happening at the same as the audio you want to use. Spectral Repair acts both on frequency and amplitude domains and it’s very effective when used along with RX’s impressive zooming features and the lasso tool also works wonders for precise selection of the audio to be processed. It can do attenuation of the undesired and also replace it altogether with the surrounding material, which is specially useful on polishing solo recordings of acoustic guitars, close-mic'd strings and vocals, taking the trash out without hurting the content. Spectral Repair can only process a small bit of material so it is a laborious yet ultimately rewarding task that can save bad recordings but also take good recordings to near perfection.
- Deconstruct (advanced only): Along with Spectral Repair, Deconstruct is one of the hardest tools to understand and master despite its limited of controls. It breaks the audio to “tonal” and “noise” components, allowing you to dial the amount of each one, radically changing the sound of a recording. Simply put, this module lets you isolate background noises on a musical recording or just take the music away and leave the noise, to some extent at least. Very interesting module to play around and learn what it considers as tonal and noise - also a good way to deal with the desired-undesired balance when Spectral Repair failed to achieve the desired results.
- De-reverb: Now available on the standard version, the De-reverb module is one of RX’s finest tools. With a simple and uncomplicated layout, De-reverb has a powerful “learn” function that reads the incoming audio and splits what it considers to be the reverberant components so the user can adjust the amount of reverb through 4 bands dry/wet bands that covers the frequency spectrum (low, low-mid, mid-high, high). There’s also a couple of handy functions such as the “enhance dry signal” that further mitigates the reverb and the tail length adjustment which is great when you don’t want to take everything away.
- Leveler/Loudness (advanced only): Leveler almost feels like cheating. It’s basically a gain-rider that works with the...rider! Set the target RMS and let it do its magic. Loudness is Leveler on a “static mode” i.e. no gain riding, so it just sets levels according to seven loudness standards adopted by the industry, which is good for quick conversion jobs where you just have to send finished audio to a client that asked for some specific loudness standard. They’re also very useful when adjusting lengthy material. I’ve some documentaries in the past where I had to deal with tons of different recording situations and Leveler would save me a ton of time on pre-editing - definitely looking forward to the next gig, it will get some good use.
- EQ Match (advanced only): I was introduced to iZotope’s EQ matching technology on Ozone and for music production it was never a technique that I used frequently, or to be totally honest I almost never use unless a job really requires it. In theory you capture the overall frequency spectrum of a recording and apply that EQ curve to another recording, resulting in a more-or-less similar spectral content. Not something I’d want often when doing music production, although I know of some cabinet-emulation freaks that make good use of this technique. However, things were different with RX, largely due to the very nature of the works I’ve done with it and the overall focus of the application. In that regard, EQ match delivers very good results with minimum effort. It’s interface is dead simple and the process revolves basically around “learning” the spectrum from one audio region and applying it to the other. This module proves to be very useful for dealing with the situation I described above on my comments about the Leveler: it’s great to homogenize radically different audio recordings. Coupled with Leveler and Ambience match, EQ match is great to nudge a sound into the direction you want. Nevertheless, this is something that operates within obvious constraints and you’ll not turn a recording around 180 degrees, but you can definitely help it sound more coherent, adding to the overall cohesion of the program material.
- Ambience Match (advanced only): Similar in principle to the EQ match, but more ambitious in its scope, Ambience match tries to make the acoustics of different recordings more close to each other. Just like it’s EQ sibling, Ambience Match is very simple to use - capture one area’s ambience and apply it to the desired target, and just like EQ match it is also great to level out differences in recording when homogeneity is required.
- Time & Pitch* (*pitch contour - advanced only): As the name says, this module can do time and pitch adjustments and they can be linked or unlinked to each other. The guys at iZotope have a fair share of expertise here since the Radius days and it’s not different this time around.
- Plugin: A plugin host so the user can have their favorite Audio Units and VSTs inside RX. The only problem here is that the plugins are not capable of running on real-time and will act like RX modules, which means you have to use the preview function to listen to the changes before committing to them. Nevertheless a very useful feature despite all shortcomings of offline processing.
- Gain: As the name says - plain gain adjustment for your volume needs. It has to be here although a bit redundant since you can use the clip gain line to make fine gain adjustments at the pre-module stage, but Gain comes in handy for the post-module processing adjustments and it is also useful with the module chain.
- Corrective EQ - Easy to use and very effective, this is basically the proven and reliable Ozone equalizer minus the matching and real-time frequency analyzer functions. This equalizer provides six parametric filters and low/high pass filters and operates on both linear and minimum phase. It sounds very pristine, with superb accuracy, a real text-book implementation. Very good to have within the context of audio repair suite.
- Channel Ops (azimuth and extract center - advanced only) - A utility module to adjust the stereo field, allowing the user to raise/lower left or right channel, along with phase and azimuth adjustments. There’s also a “extract center” function to isolate mid from side on stereo recordings.
- Resample - This module provides sample rate conversions using one of the cleanest algorithms out there (according to this huge and ever-increasing database SRC Comparisons), with a special steep low-pass filter developed by iZotope to keep aliasing away.
- Dither - Last but not least, dithering for your bit-reduction needs with all the necessary options one needs to safely convert with the best quality, powered by iZotope’s in-house MBIT+ algorithm.
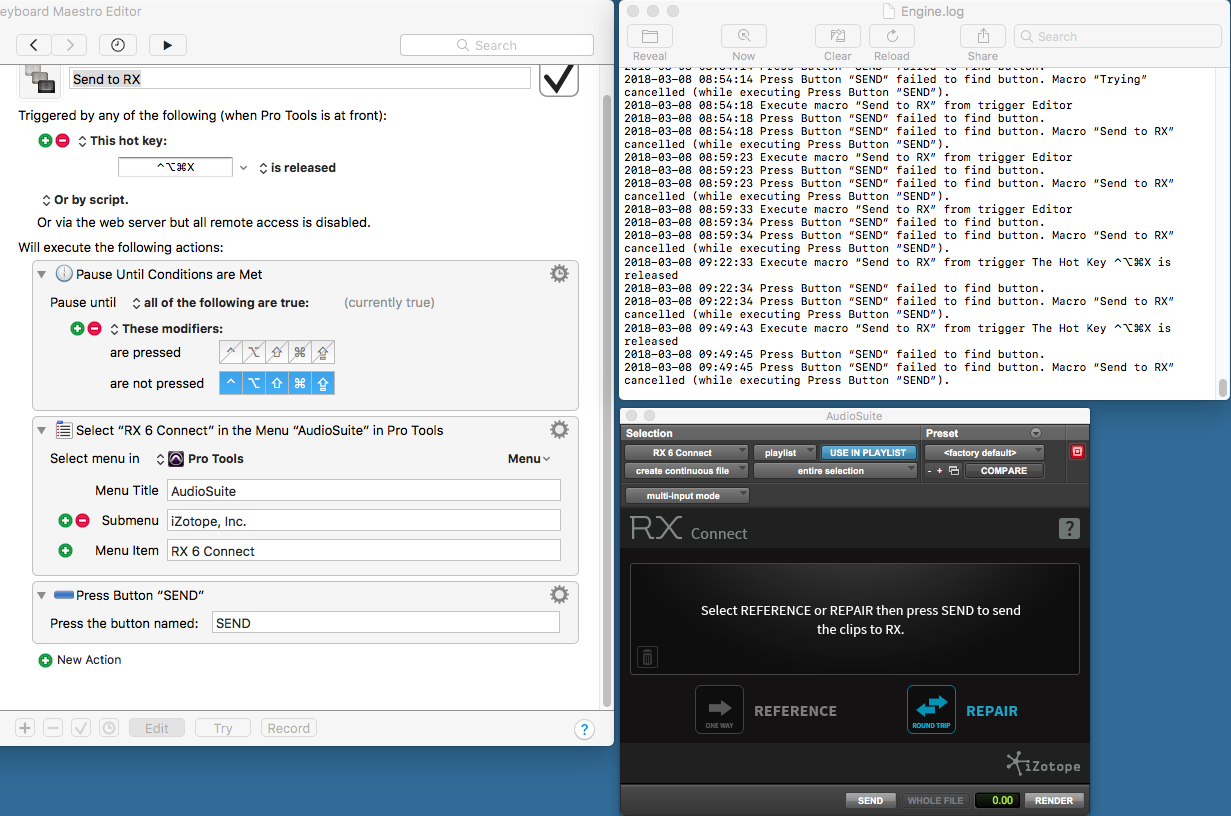
RX Connect - DAW integration
Using RX Connect, which links your DAW and RX, cleaning audio with RX without leaving your DAW is quite a breeze. You just need highlight the parts of your audio, select Connect from the Audio Suite menu and send the region to RX as a “round trip”, which means I’ll treat the audio with RX then send it back to Pro Tools. RX will open up, apply the desired processing, click the “send back” button and commit the changes with RX Connect. It hardly takes a few extra clicks than using the standalone app and I’d say it’s very much worth it. To test the RX-DAW integration I took a 2-track live recording of a music performance with vocals and acoustic guitar, which had over an hour of material to be edited. The performance was very good, but plagued with technical issues so I had to remove hiss from the not-so-quiet noise floor, clicks/crackles from bad connector on the guitar, attenuate clipping on the vocals track, rebalance the piezo mic from the acoustic guitar. In short, the material had to be repair and made viable for mixing and mastering, and so I went hundreds of times through the processes of “select audio - RX connect to send to RX app - work miracles on RX - send back function - render”. Over and over and over again until all clips were crystal-clear. Integration with Pro Tools with pretty flawless in that regard, and I’ve found myself working quite fast - RX’s stability was great in that regard. One thing that helped me to work easier was RX’s “monitor” plugin, which allowed me to monitor the changes through your mixing chain.
The Scores
Sound quality - 5/5: Arguably the best sounding set of tools in the audio repair segment, RX can do things that are borderline science-fiction and will challenge common beliefs of what is possible and what is not. All around RX offers the best quality processing you can get but some of the modules really stand out, like the remarkables De-click and De-clip and also the extremely competent De-noise. De-clip really saved recordings that I initially considered unviable for anything serious, it’s really something special and would do great on a simple plugin on it’s own - I think I’ve said the same thing a number of times to be honest...but a man can dream. De-reverb and Ambience match are also worth mentioning and they’re arguably the best tools on their categories, providing spectacular results. Overall the sound quality of the modules are amazing, they became industry standards for very good reasons and will be very hard to be topped.
Ease of use - 5/5: RX is mostly accessible and easy to use, I say “mostly” because some of the modules have a steeper learning curve than others. I’d say RX is “easy as it can be” and in that regard it is expected that removing the room fan with Spectral Repair poses a tougher challenge than removing simple clicks or lowering a high noise floor without killing your top end. On most occasions RX is in fact totally straightforward - the De-noise, EQ match and De-Reverb modules are surprisingly easy for what they can do and achieve. The standalone app is really a breeze to use, with clean and uncluttered interfaces not only for the main editor but also for all the modules Using RX inside a DAW with the Connect plugin is a bit more laborious since you have to set up the Monitor plugin and RX’s output accordingly, but it’s nothing complicated. There’s also the possibility to use the provided plugins for most of RX modules as regular plugins in your DAW and that works well on some occasions but since the Connect/Monitor setup was so easy I ended up rarely using them. I should also say that the documentation is nothing but stellar, with a big HTML help file that covers everything in great detail, with a very clear language that really helps to get the best out of each module and of RX as a whole. If that wasn’t enough, iZotope recently released a website with a ton of tricks called the “RX cookbook”, with a good search mechanism that allows users to sort articles according to each RX version, module or real-world application - definitely very helpful resource that adds further points to RX’s ease of use.
Features - 5/5: Both standard and advanced versions are spectacular in terms of how much they pack. Needles to say that the advanced version provides greater depth and audio processing options that makes the “advanced” label a very deserved and rightful one, but standard version is also very well featured and will cover most common scenarios. Nevertheless, in true Gearslut fashion, I’d totally welcome less offline processing and more real-time action. I can understand the reasons behind “not having so much online processing” but it’s not a distant reality as computers are always getting more powerful and in that regard I’d like to see better online processing with lower latencies in the future.
Bang for buck - 5/5: Once you start using it, RX quickly reveals itself as an immensely valuable set of tools and it’s hard to imagine life without it. However, the gap between standard and advanced version still feels like it’s a bit too wide despite iZotope’s efforts to narrow it. Nonetheless, RX Standard offers an unbelievable bang for your buck and I would give it a six out of five stars if such score was possible. On the other hand, I feel like the bucks required for the advanced version are a bit too much and I’d welcome some further licensing options for single modules, two/three modules combos and anything that lessens the burden our pockets. Pricing debates aside and regardless of which version you end up choosing, RX is an investment that quickly proves to be very worth making and RX really inspires a lot of confidence.
The verdict:
 iZotope’s RX 5 arrives on its fifth iteration with as an extremely well rounded and matured solution to rescue your recordings most problematic moments and to save yourself a world of troubles that you’d end up without it. RX is the closest thing to insurance when it comes to audio recordings and it feels like having a safety net when you have no options other than face the situation and roll with that problematic recording. That might sound a bit dramatic but it’s definitely the case when you starting using it and the miracles start to line up in front of you. What RX can do can not be described in other terms. It’s really a decisive tool that can make a huge difference, both when turning bad recordings into something that can actually be used and when some polish is needed on less than stellar recordings. Once you realize its power, RX becomes almost as necessary and indispensable as your DAW.
iZotope’s RX 5 arrives on its fifth iteration with as an extremely well rounded and matured solution to rescue your recordings most problematic moments and to save yourself a world of troubles that you’d end up without it. RX is the closest thing to insurance when it comes to audio recordings and it feels like having a safety net when you have no options other than face the situation and roll with that problematic recording. That might sound a bit dramatic but it’s definitely the case when you starting using it and the miracles start to line up in front of you. What RX can do can not be described in other terms. It’s really a decisive tool that can make a huge difference, both when turning bad recordings into something that can actually be used and when some polish is needed on less than stellar recordings. Once you realize its power, RX becomes almost as necessary and indispensable as your DAW. Recommended for absolutely all professionals or studios dealing with any aspect of audio, be it on post-production for other medias or on mixing and mastering music. RX is also an indispensable tool for professionals doing forensic, restoration and archiving works.
Gearslutz Should I Buy Izotope Rx 7 Audio Editor
Post-script: As I was on the closing stages of writing down this review, iZotope recently launched Dialog De-Noise, De-clip, De-click and De-hum as 4-plugin package called “RX Plugin Pack” that furthers the options for new users. As I’ve mentioned above I believe some of those would make fine products on their own, especially Dialog De-Noise and the incredible De-clip, and this package is a very welcome addition to their audio repair tools and a good entry ticket to RX’s universe. At $129 (MSRP) the pack definitely has some great value but I missed an upgrade path to RX Standard at a friendly price. As their past actions have show, iZotope certainly is not afraid of changing their pricing and distribution strategies so it will not come as a surprise if we see that happening at some point. Nevertheless, I really have to applaud the effort they’re making to make these tools available to a wider range of people and their respective budget limitations.
Comments are closed.